Federal Rulemaking Process
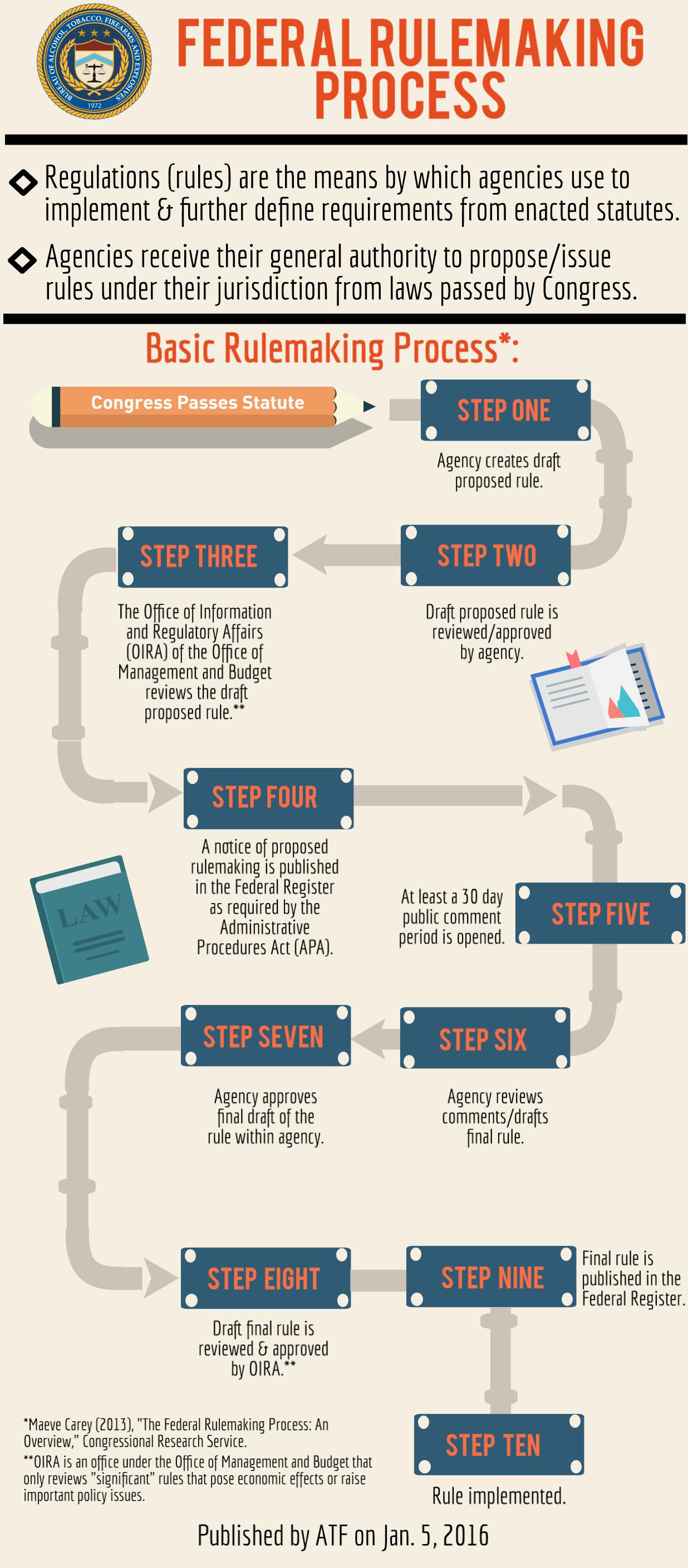
- Regulations (rules) are the means by which agencies use to implement and further define requirements form enacted statutes.
- Agencies receive their general authority to propose/issue rules under their jurisdiction from laws passed by Congress.
Basic Rulemaking Process*:
- Congress Passes Statute
- Step One: Agency creates draft proposed rule.
- Step Two: Draft proposed rules is reviewed/approved by agency.
- Step Three: The Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA) of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) reviews the draft proposed rule.**
- Step Four: A notice of proposed rulemaking is published in the Federal Register as required by the Administratie Procedures Act (APA).
- Step Five: At least a 30 day public comment period is opened.
- Step Six: Agency reviews comments/drafts final rule.
- Step Seven: Agency approves final draft of the rule within the agency.
- Step Eight: Draft final rule is reviewed and approved by OIRA.**
- Step Nine: Final rule is published in the Federal Register.
- Step Ten: Rule is implemented.
* Maeve Carey *2013), "The Federal Rulemaking Process: An Overview," Congressional Research Service.
** OIRA is an office under the Office of Management and Budget that only reviews "significant" rules that pose economic effects or raise important policy issues.
Published by ATF on January 5, 2016

